Our Services
Dentists
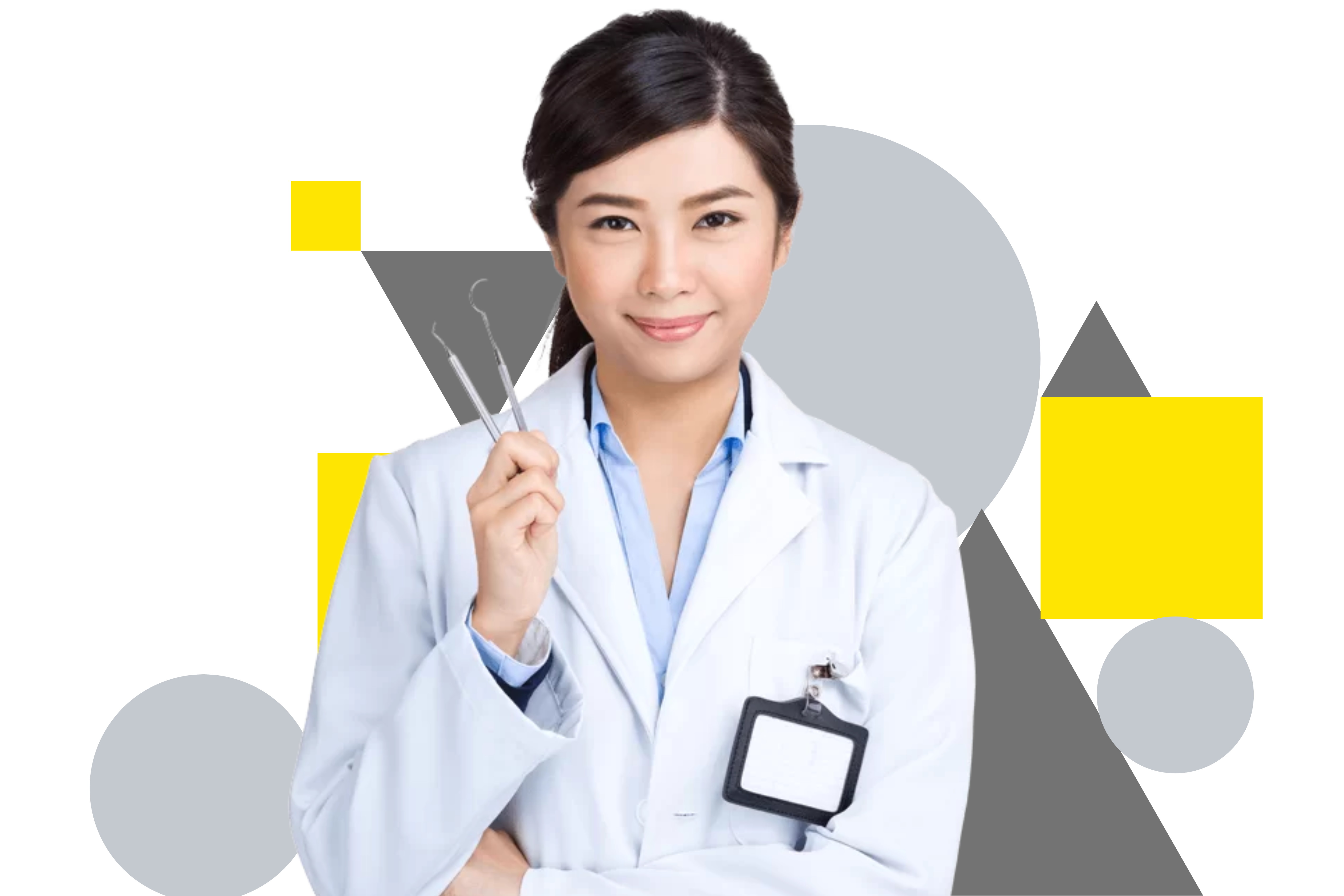

Dentists in Australian society play a crucial role in promoting oral health and providing essential dental care services to the population.
Here are some key roles that dentists fulfill:
Dentists educate patients about proper oral hygiene practices, including brushing, flossing, and maintaining a healthy diet. They emphasize the importance of regular dental check-ups and cleanings to prevent common dental problems such as tooth decay, gum diseases, and bad breath.
Dentists educate patients about proper oral hygiene practices, including brushing, flossing, and maintaining a healthy diet. They emphasize the importance of regular dental check-ups and cleanings to prevent common dental problems such as tooth decay, gum diseases, and bad breath.
Dentists are often available for emergency dental care to address sudden pain or injuries related to teeth or gums. They provide immediate relief for issues like severe toothaches or broken teeth.
Dentists play an active role in promoting good oral health practices within the community through educational programs at schools or community centers. They raise awareness about the importance of oral hygiene habits from an early age to prevent future dental problems.
Some dentists specialize in specific areas such as orthodontics (alignment of teeth), periodontics (gum diseases), endodontics (root canal treatment), prosthodontics (restorative dentistry), pediatric dentistry (children’s dental care), oral surgery, etc., providing specialized treatments beyond general dentistry.
Many people seek cosmetic procedures like teeth whitening to enhance their smile’s appearance. Dentists offer professional teeth whitening services and other cosmetic procedures to improve the aesthetics of patients’ teeth.
Dentists often work in collaboration with other healthcare professionals, such as physicians, orthodontists, oral surgeons, and dental hygienists. They coordinate care for patients who require multidisciplinary treatment or have underlying medical conditions that may impact their oral health.
Dentists contribute to research efforts aimed at improving dental treatments, technologies, and materials. They stay updated on the latest advancements in dentistry to provide the best possible care for their patients.
Overall, dentists play a vital role in Australian society by promoting good oral health practices, diagnosing and treating dental conditions, providing preventive care services, and enhancing the overall well-being of individuals through quality dental care.
Contributions of Overseas-trained Dentists in Australia
Overseas-trained dentists make significant contributions to the dental profession in Australia.

Addressing Workforce Needs
Overseas-trained dentists help address workforce shortages, particularly in areas where there is a high demand for dental services or a shortage of local dentists. They fill gaps in the dental workforce, ensuring that communities have access to essential oral healthcare.

Diverse Skills and Experiences
Overseas-trained dentists bring diverse skills, knowledge, and experiences from their home countries. This diversity enriches the dental profession by introducing different perspectives and approaches to patient care.

Specialist Expertise
Many overseas-trained dentists have specialized training or expertise in specific areas of dentistry such as orthodontics, periodontics, endodontics, prosthodontics, oral surgery, and more. Their specialized skills contribute to providing comprehensive care options for patients within the Australian healthcare system.

Multilingual Abilities
Dentists who are fluent in languages other than English can effectively communicate with patients from diverse cultural backgrounds who may have limited English proficiency. This helps improve patient satisfaction and ensures effective communication during treatment planning and delivery.

Cultural Competence
Overseas-trained dentists often possess cultural competence due to their exposure to different cultures through their training or practice abroad. This enables them to understand and respect the unique needs of patients from various cultural backgrounds.

Research Collaboration
Many overseas-trained dentists engage in research collaborations with local researchers and institutions within Australia's dental community. Their involvement contributes to advancing knowledge and improving dental practices through research studies focused on various aspects of oral health.

Supporting Rural/Remote Areas
Overseas-trained dentists often work in rural or remote areas where there is a shortage of local practitioners willing to practice outside major cities or metropolitan regions. This helps ensure that people living outside urban centers also have access to quality dental care services.
It’s important to note that overseas-trained dentists must meet the registration requirements set by the Dental Board of Australia (DBA) and undergo an assessment process to ensure their qualifications and skills align with Australian standards. This ensures that they provide safe and competent dental care to patients in Australia.
Overall, overseas-trained dentists play a vital role in meeting the dental healthcare needs of Australians, contributing their expertise, diversity, and cultural competence to enhance oral health services across the country.
Here are some key ways in which they contribute:
Overseas-trained dentists help address workforce shortages, particularly in areas where there is a high demand for dental services or a shortage of local dentists. They fill gaps in the dental workforce, ensuring that communities have access to essential oral healthcare.
Overseas-trained dentists bring diverse skills, knowledge, and experiences from their home countries. This diversity enriches the dental profession by introducing different perspectives and approaches to patient care.
Many overseas-trained dentists have specialized training or expertise in specific areas of dentistry such as orthodontics, periodontics, endodontics, prosthodontics, oral surgery, and more. Their specialized skills contribute to providing comprehensive care options for patients within the Australian healthcare system.
Dentists who are fluent in languages other than English can effectively communicate with patients from diverse cultural backgrounds who may have limited English proficiency. This helps improve patient satisfaction and ensures effective communication during treatment planning and delivery.
Overseas-trained dentists often possess cultural competence due to their exposure to different cultures through their training or practice abroad. This enables them to understand and respect the unique needs of patients from various cultural backgrounds.
Many overseas-trained dentists engage in research collaborations with local researchers and institutions within Australia’s dental community. Their involvement contributes to advancing knowledge and improving dental practices through research studies focused on various aspects of oral health.
Overseas-trained dentists often work in rural or remote areas where there is a shortage of local practitioners willing to practice outside major cities or metropolitan regions. This helps ensure that people living outside urban centers also have access to quality dental care services.
It’s important to note that overseas-trained dentists must meet the registration requirements set by the Dental Board of Australia (DBA) and undergo an assessment process to ensure their qualifications and skills align with Australian standards. This ensures that they provide safe and competent dental care to patients in Australia.
Overall, overseas-trained dentists play a vital role in meeting the dental healthcare needs of Australians, contributing their expertise, diversity, and cultural competence to enhance oral health services across the country.

Registration of Dentists
In Australia, dentists must be registered with the Dental Board of Australia (DBA) in order to practice legally. The DBA is a national regulatory authority that operates under the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA). Here are some key points regarding the registration process for dentists in Australia:

1. Qualifications
Dentists must have completed an approved dental program and obtained a recognized dental qualification. The most common qualification is a Bachelor of Dental Surgery (BDS) or an equivalent degree from a recognized dental school.
2. English Language Proficiency
Overseas-trained doctors need to demonstrate English language proficiency by providing evidence such as achieving satisfactory scores in approved English language tests like IELTS or OET.

3. Assessment Process
Overseas-trained dentists seeking registration in Australia need to undergo an assessment process conducted by the Australian Dental Council (ADC). The ADC assesses their qualifications, skills, knowledge, and clinical competence to ensure they meet Australian standards for dental practice.

4. National Examination
After successfully completing the assessment process, overseas-trained dentists are required to pass the National Examination administered by the ADC before they can apply for registration with the DBA.

5. Criminal History Check
All applicants for dentist registration in Australia are required to undergo a criminal history check as part of their application process.

6. Continuing Professional Development (CPD)
Once registered, dentists are expected to engage in ongoing professional development activities to maintain and enhance their skills and knowledge throughout their careers.
It’s important to note that the registration process and requirements may vary for different categories of doctors, such as specialists, general practitioners (GPs), or those seeking to work in specific areas of practice.
The MBA and AHPRA ensure that all registered doctors adhere to professional standards, ethical guidelines, and codes of conduct. They also have mechanisms in place to investigate complaints or concerns regarding a doctor’s practice and take appropriate action if necessary.
Overall, the registration process for doctors in Australia aims to uphold high standards of medical practice, protect public safety, and ensure that healthcare services are delivered by qualified professionals who meet the required competencies.
Assessment Process of Overseas-trained Dentists in Australia
The assessment process for overseas-trained dentists in Australia is conducted by the Australian Dental Council (ADC). The ADC is responsible for assessing the qualifications, skills, knowledge, and clinical competence of dentists trained outside of Australia to ensure they meet the standards required for dental practice in Australia. Here are some key points regarding the assessment process:
The assessment process for overseas-trained dentists in Australia is conducted by the Australian Dental Council (ADC). The ADC is responsible for assessing the qualifications, skills, knowledge, and clinical competence of dentists trained outside of Australia to ensure they meet the standards required for dental practice in Australia. Here are some key points regarding the assessment process:
1. Application
Overseas-trained dentists interested in practicing in Australia must submit an application to the ADC. The application typically includes providing detailed information about their dental qualifications, professional experience, and other relevant documentation.
2. Preliminary Assessment
Upon receiving the application, the ADC conducts a preliminary assessment to determine if an applicant's qualifications are substantially equivalent to those of an Australian-trained dentist. This involves reviewing educational credentials and assessing whether they meet certain criteria set by the ADC.
3. Written Examination
Upon receiving the application, the ADC conducts a preliminary assessment to determine if an applicant's qualifications are substantially equivalent to those of an Australian-trained dentist. This involves reviewing educational credentials and assessing whether they meet certain criteria set by the ADC.
4. Practical Examination
Following successful completion of the written examination, candidates proceed to a practical examination that evaluates their clinical skills and competence in performing dental procedures under simulated conditions.
5. English Language Proficiency
As part of their overall assessment process with the ADC, overseas-trained dentists must also demonstrate English language proficiency by meeting specific requirements set by AHPRA and DBA. This typically involves achieving satisfactory scores on approved English language tests such as IELTS or OET.
6. Clinical Training
It’s important to note that each individual’s assessment process may vary depending on factors such as their country of origin and specific circumstances related to their education and experience. For more detailed information on the assessment process for overseas-trained dentists in Australia, it is recommended to visit the Australian Dental Council’s website (www.adc.org.au) or contact them directly. They can provide the most up-to-date and accurate information regarding the assessment process and requirements for overseas-trained dentists seeking registration in Australia.
The National Examination for Overseas-trained Dentists
The National Examination for overseas-trained dentists in Australia is an assessment conducted by the Australian Dental Council (ADC). It is a requirement for overseas-trained dentists who have successfully completed the ADC’s preliminary assessment and are deemed eligible to proceed to the examination stage. Here are some key points regarding the National Examination:
Purpose
The National Examination aims to assess the clinical skills, knowledge, and competence of overseas-trained dentists in order to ensure they meet the standards required for dental practice in Australia.
Format
The examination consists of both written and practical components.
This component assesses theoretical knowledge across various areas of dentistry, including oral medicine, oral surgery, prosthodontics, periodontics, endodontics, orthodontics, pediatric dentistry, and more. It typically involves multiple-choice questions or short-answer questions.
This component evaluates candidates’ clinical skills and competence in performing dental procedures under simulated conditions. It may involve tasks such as restorative procedures (fillings), crown preparations on typodonts (artificial teeth), radiographic interpretation exercises, or other relevant clinical scenarios.
Preparation
Candidates are encouraged to prepare thoroughly for the examination by reviewing their knowledge across different areas of dentistry covered in the syllabus provided by the ADC. They may also consider attending preparatory courses or seeking guidance from experienced professionals familiar with Australian dental practice standards.
Examination Dates and Locations
The ADC conducts multiple sittings of the National Examination throughout each year at designated locations within Australia.
Results and Outcome
After completing both components of the examination, candidates receive their results indicating whether they have passed or failed each section separately.
Clinical Training Requirements
Depending on individual assessments conducted by ADC during preliminary stages or after completion of examinations, some candidates may be advised to undertake additional clinical training or supervised practice before being eligible for full registration as a dentist in Australia.
It’s important to note that the National Examination is just one component of the overall assessment process for overseas-trained dentists seeking registration in Australia. Successful completion of the examination, along with meeting other requirements such as English language proficiency and any additional training or experience deemed necessary, is necessary for obtaining full registration as a dentist in Australia. For more detailed information on the National Examination and its specific requirements, it is recommended to visit the Australian Dental Council’s website (www.adc.org.au) or contact them directly. They can provide comprehensive and up-to-date information regarding the examination process for overseas-trained dentists in Australia.
RPS Expertise in Dentists’ Registration
RPS Migration Services has experience in assisting overseas-trained dentists with the preparation of documents to make them eligible for registration in Australia. Having professional assistance can be valuable in navigating the complex process of meeting the requirements set by regulatory bodies such as the Australian Dental Council (ADC) and the Dental Board of Australia (DBA). RPS Migration Services can likely provide guidance and support throughout various stages, including:
Assisting with gathering and organizing all necessary documentation required for the preliminary assessment conducted by ADC.
Helping dentists compile their educational credentials, work experience records, English language proficiency test results, and other relevant documents required for registration.
Providing guidance on completing application forms accurately and ensuring all necessary information is included.
Offering advice on preparing for the National Examination administered by ADC, including recommending study materials or preparatory courses.
Assisting with any additional requirements identified during the assessment process, such as clinical training or supervised practice if deemed necessary.
It’s important to note that while RPS Migration Services may have experience in supporting overseas-trained dentists through this process, it is always recommended to verify their expertise and ensure they are knowledgeable about current regulations and requirements set by ADC and DBA. Additionally, it’s advisable to consult multiple sources of information such as official websites of regulatory bodies like ADC or DBA to stay updated on any changes or updates regarding registration processes for overseas-trained dentists in Australia. Remember that successful registration ultimately depends on meeting all eligibility criteria established by regulatory authorities within Australia’s dental profession.
