Our Services
Nurses

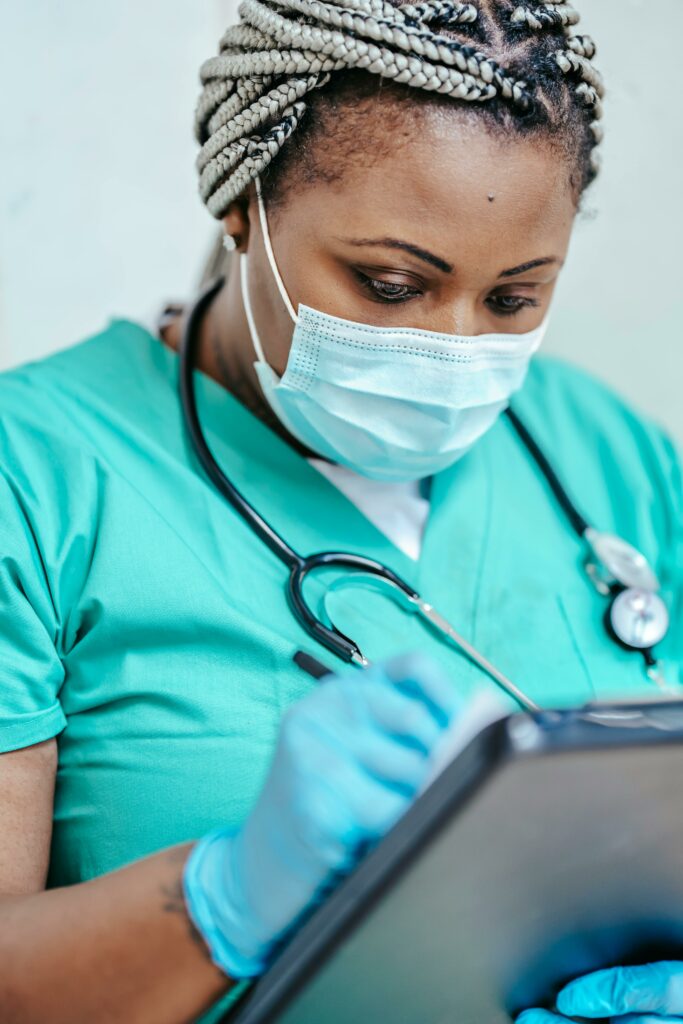
Nurses play a crucial role in the Australian healthcare system, providing essential care and support to patients across various settings. They are highly valued for their expertise, compassion, and dedication to improving patient outcomes.
In hospitals, nurses are at the forefront of patient care, working closely with doctors and other healthcare professionals. They assess patients’ conditions, administer medications, monitor vital signs, and provide treatments. Nurses also play a vital role in coordinating patient care plans and ensuring effective communication between different members of the healthcare team.
Beyond hospitals, nurses contribute significantly to community health by working in clinics, aged care facilities, schools, and home health settings. They provide preventive care services such as vaccinations and health screenings while educating individuals on maintaining good health practices.
Nurses also have a significant impact on mental health support in Australia. Mental health nurses work alongside psychiatrists and psychologists to assess patients’ mental well-being and develop treatment plans. They offer counseling services, administer medications for mental illnesses when necessary, and provide ongoing support for individuals experiencing mental health challenges.
In addition to direct patient care roles, nurses often take on leadership positions within healthcare organizations. Nurse managers oversee nursing staff schedules and ensure quality standards are met. Nurse educators train future generations of nurses through teaching programs at universities or vocational institutions.
Australia recognizes the importance of nursing as a profession by offering competitive salaries for registered nurses (RNs) along with benefits such as paid leave entitlements and professional development opportunities. Nurses can also pursue further specialization through postgraduate studies or gain advanced practice roles such as nurse practitioners or clinical nurse specialists.
The demand for skilled nurses remains high across Australia due to factors like an aging population requiring increased healthcare services. This creates ample job opportunities for both local graduates as well as internationally qualified nurses seeking migration pathways into Australia’s healthcare workforce.
Overall, the role of nurses in Australian healthcare is indispensable – they provide compassionate care while promoting wellness within diverse communities throughout the country.
Registration of Nurses
1. English Language Proficiency
Demonstrate English language proficiency by achieving the required scores in an approved English language test such as IELTS or OET.

2. Qualification Assessment
Have your nursing qualifications assessed by the Australian Nursing and Midwifery Accreditation Council (ANMAC) or another authorized assessing authority to ensure they meet Australian standards.

3. Apply for AHPRA Registration
Apply for registration with the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA), which is responsible for regulating healthcare professionals in Australia. The specific registration type will depend on your qualifications and experience.

4. Provide Supporting Documents
Submit all necessary documents, including identification, proof of education, transcripts, work experience certificates, and evidence of English language proficiency.

5. Criminal History Check
Undergo a criminal history check to ensure you meet the character requirements set by AHPRA.

6. Undergo Accredited Program
If your qualifications do not directly align with Australian standards, you may need to complete an accreditation program approved by AHPRA to bridge any gaps in knowledge or skills.
7. National Board Decision
Once all requirements are met and documents submitted, the Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia (NMBA) will assess your application for registration based on their guidelines.

8. Obtain Visa (if applicable)
If you are applying from overseas, you will also need to obtain an appropriate visa that allows you to work as a nurse in Australia.
Seeking guidance from RPS Migration Services who is specializing in healthcare migration services can be beneficial throughout this process as we can provide personalized advice based on your individual circumstances and assist with navigating any complexities that may arise.
Accredited Programs of AHPRA
Outcomes-Based Assessment
Outcomes-Based Assessment (OBA) is an assessment approach used in nursing education and professional development to evaluate a nurse’s competency and performance based on specific outcomes or standards. It focuses on assessing the practical application of knowledge, skills, and attitudes in real-life situations.
In the context of nursing, OBA aims to ensure that nurses are competent and capable of providing safe and effective care to patients. It goes beyond theoretical knowledge by assessing how well nurses can apply their skills in clinical practice.
Here are some key aspects of Outcomes-Based Assessment for nurses:
OBA is based on predetermined competency standards that outline the expected knowledge, skills, attitudes, and behaviors required for nursing practice. These standards may be set by regulatory bodies or professional organizations.
The assessment criteria are clearly defined within each competency standard. They describe observable behaviors or actions that demonstrate competence in a particular area of nursing practice.
OBA emphasizes authentic assessments that reflect real-world scenarios encountered by nurses in their daily work environments. This can include direct observation of clinical skills, case studies, simulations, written assignments, reflective journals, or oral presentations.
Ongoing feedback is an integral part of OBA to support learning and improvement. Nurses receive constructive feedback from assessors who observe their performance during assessments. This feedback helps identify strengths and areas for development while encouraging self-reflection.
OBA promotes lifelong learning by identifying areas where further development may be needed to meet evolving healthcare demands or changes in practice guidelines.
Nurses are expected to demonstrate their ability to apply evidence-based practices when delivering care during assessments as part of promoting quality patient outcomes.
OBA often involves collaboration between educators/assessors and practicing nurses to ensure alignment with current best practices while addressing individual learning needs effectively.
By using an Outcomes-Based Assessment approach, nursing education programs and professional development initiatives can ensure that nurses are competent, skilled, and capable of delivering safe and high-quality care to patients. It helps maintain standards of practice while promoting continuous improvement in nursing skills and knowledge.
NCLEX AND OSCE Preparation
We are excited to announce that RPS Migration Services, in collaboration with Australian Certified Trainers, now offers comprehensive NCLEX and OSCE preparation programs specifically designed for overseas-trained nurses.
The NCLEX (National Council Licensure Examination) is a standardized exam that assesses the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level nursing practice in the United States and Canada and now in Australia. Our NCLEX preparation program is tailored to help nurses confidently prepare for this challenging exam. With expert guidance from experienced trainers, we provide comprehensive content review, practice questions, test-taking strategies, and simulated exams to enhance your chances of success. The OSCE (Objective Structured Clinical Examination) is an assessment method used to evaluate clinical competence in nursing. Our OSCE preparation program focuses on refining your clinical skills through hands-on training sessions conducted by qualified trainers. We simulate real-life scenarios commonly encountered in healthcare settings, providing you with valuable practice and feedback to excel in the OSCE examination. Our collaboration with Australian Certified Trainers ensures that our programs are delivered by professionals who have extensive experience working within the nursing field. They possess a deep understanding of the requirements and expectations of both the NCLEX and OSCE examinations. At RPS Migration Services, we understand that preparing for these exams can be daunting for overseas-trained nurses seeking registration or employment opportunities abroad. That is why our aim is to provide you with comprehensive support throughout your journey. We not only assist you with migration services but also equip you with the necessary tools and resources needed to succeed in these critical assessments. By choosing our NCLEX and OSCE preparation programs, you can benefit from:- Expert guidance from experienced trainers
- Comprehensive content review
- Extensive practice questions
- Test-taking strategies
- Simulated exams mirroring actual testing conditions
- Hands-on training sessions focusing on clinical skills development
We are committed to helping overseas-trained nurses achieve their professional goals by providing top-notch support every step of the way. With our NCLEX and OSCE preparation programs, you can enhance your knowledge, skills, and confidence to excel in these examinations and pursue a successful nursing career abroad.
Contact us today to learn more about how RPS Migration Services, in collaboration with Australian Certified Trainers, can assist you in preparing for the NCLEX and OSCE examinations. Let us be your trusted partner on your journey towards professional success.Get assessed now!



University Programs
Australian universities offer Bachelor of
Nursing programs as well as Master’s degree programs in nursing that can lead
to AHPRA registration, enabling both domestic and overseas-trained nurses to
work as registered nurses in Australia.
The Bachelor of Nursing program is typically a three-year undergraduate degree that provides comprehensive theoretical knowledge and practical skills necessary for nursing practice. It covers various areas such as anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, clinical skills development, and healthcare ethics. Upon completion of the program and meeting the registration requirements set by AHPRA, graduates can apply for nursing registration.


Credit transfer is a process where previous academic credits are recognized by the university towards fulfilling certain course requirements. This means that if you have completed relevant studies or have prior learning experiences that align with specific subjects within the nursing program curriculum, you may be eligible for credit transfer. This recognition helps shorten the overall duration of your study by exempting you from repeating certain coursework.
For those who already hold a bachelor’s degree in another field or have completed relevant nursing qualifications from their home country, pursuing a Master’s degree in nursing can be an option. The Master’s program allows individuals to build upon their existing knowledge and skills while gaining advanced expertise in specific areas of nursing practice. This pathway may also provide credit transfer options based on previous qualifications or experience, which can reduce the duration of study required.
It is important to note that credit transfer policies vary between universities and individual circumstances are assessed on a case-by-case basis. Therefore, it is advisable to contact your chosen university directly to inquire about their specific credit transfer policies and procedures.
By offering both undergraduate and postgraduate pathways with potential credit transfers available at some institutions across Australia, universities aim to provide flexibility for aspiring nurses while ensuring they receive quality education aligned with national standards. These programs equip students with essential knowledge and practical skills required for successful careers in nursing while facilitating their journey towards AHPRA registration.
The Trans-Tasman Mutual Recognition (TTMR) agreement is a beneficial pathway for nurses registered in New Zealand to have their registration recognized by AHPRA in Australia, and vice versa. This agreement allows for the mutual recognition of professional qualifications between Australia and New Zealand.
Under TTMR, nurses who are registered in either country can apply for registration in the other country without having to undergo a full assessment process. This means that if you are a nurse registered with the Nursing Council of New Zealand, you can apply for registration with AHPRA in Australia through an expedited process.
Similarly, nurses registered with AHPRA can have their registration recognized by the Nursing Council of New Zealand through TTMR. This facilitates ease of mobility and employment opportunities for nurses between both countries.
In addition to New Zealand, TTMR is also open to nurses from Singapore, United Kingdom (including England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland), Ireland, Canada (excluding Quebec), and the United States of America. Nurses from these countries who hold current registration can utilize this route to have their qualifications recognized by AHPRA or the Nursing Council of New Zealand.
It’s important to note that while TTMR streamlines the registration process between these countries, there may still be some specific requirements or conditions that need to be met. It is advisable to review the guidelines provided by AHPRA or the Nursing Council of New Zealand regarding TTMR eligibility criteria and application procedures.
The Trans-Tasman Mutual Recognition agreement serves as a valuable mechanism for qualified nurses from participating countries seeking opportunities across Australia and New Zealand. It promotes professional mobility while maintaining high standards of nursing practice within both nations’ healthcare systems.
Trans-Tasman Mutual Recognition


